Many people that struggle to sleep at night will turn to Melatonin Supplements. But How Much Melatonin Is Too Much? This is actually a very good question because according to some sources, too much melatonin from supplements can affect natural melatonin production.
In fact, some researchers have concluded that the dosage of melatonin that most people get from “your typical otc melatonin supplements” is too much. Even 1 x 3mg tablet may be too much but whether this is true or not is debatable.
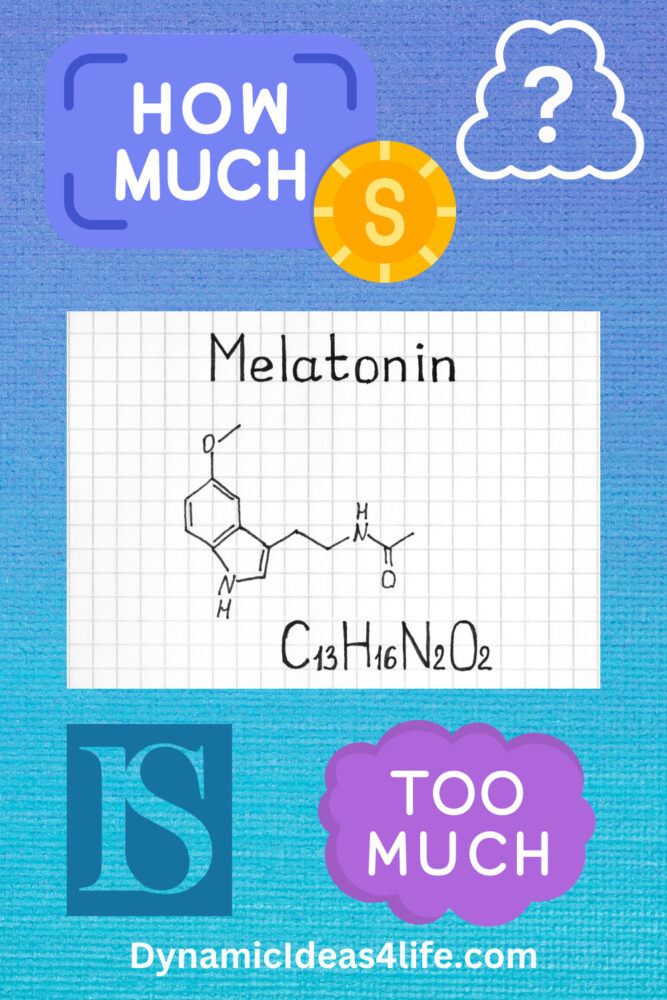
So Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain. It plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle and for this reason, it is very popular as a dietary supplement used to treat sleep disorders and other conditions.
However, while melatonin supplements are generally considered safe, it’s important to take them in the right amounts to avoid potential side effects.
But again how much melatonin is too much?
By the end of this article, we hope to give you a better understanding of how melatonin supplements work and if you do still want to take these products how to use them safely and effectively. I know some people will not want to take this information on board, but anyhow let’s get back to the question.
How Much Melatonin Is Too Much?
According to Healthline, administering melatonin at doses of 1-5 milligrams (mg) may result in seizures or other adverse effects in young children. Studies conducted in adults have used doses ranging from 1 to 10 mg, but there is no established “optimal” dosage. However, doses exceeding 30 mg are thought to pose potential harm.
So What You Should Know About Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone that is naturally produced by the pineal gland in the brain. It plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s internal clock and is essential for maintaining healthy sleep patterns. Melatonin helps to promote sleepiness at night and wakefulness during the day, making it an important hormone for those who struggle with sleep disorders or jet lag.
Despite its natural occurrence in the body though many people turn to melatonin supplements to help regulate their sleep patterns. However, the safety and efficacy of these supplements raise many questions. So much so that the use of Melatonin supplements in the United Kingdom (UK), European Union, Japan, Australia, and Canada has been outlawed. There are some exceptions where you can still get Melatonin in these countries but this does make you wonder why?
In this article, we’ll explore the functions of melatonin, its importance for sleep, and why people may choose to take melatonin supplements. We’ll also discuss how much melatonin is too much and the potential risks associated with taking too high of a dose.
By understanding the proper usage and dosage of melatonin supplements, you can ensure that you’re getting the best possible sleep while minimizing any potential risks. So let’s continue here…
What is the Recommended Melatonin Dosage?
The recommended dosage of melatonin varies depending on the individual’s age and the purpose of use.
According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM), the following are the recommended doses:
- Adults: 0.5 to 5 milligrams (mg) taken 30 minutes to an hour before bedtime.
- Children and adolescents: 0.5 to 3 mg taken 30 minutes to an hour before bedtime.
However, still, It’s important to note that the recommended dosage is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Factors such as weight, medical history, and individual sensitivity to melatonin can influence the appropriate dosage. Therefore, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional before taking melatonin supplements.
Taking too much melatonin can also pose risks. Exceeding the recommended dosage can result in side effects such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, and irritability.
Furthermore, taking extremely high doses may cause more severe complications, such as daytime sleepiness, confusion, and disorientation but perhaps the other big thing is the disruption of natural melatonin production.
This I will look to cover shortly but further to this;
What are the Potential Side Effects of Taking Too Much Melatonin?
While melatonin is generally considered safe when taken in recommended doses, taking too much of it can result in unpleasant side effects. Some of the common side effects of melatonin overdose include:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Irritability
- Stomach cramps
- Diarrhea
The severity and duration of these side effects may vary from person to person and depend on the amount of melatonin taken. Taking too much melatonin over a long period can also increase these risks.
Prolonged use of high doses of melatonin may interfere with the body’s natural production of the hormone, leading to decreased effectiveness and even dependence on the supplement.
Additionally, some studies have suggested that long-term use of melatonin may be associated with an increased risk of certain health problems, such as hormonal imbalances and mood disorders.
So, It’s important to note that there is a difference between melatonin overdose and melatonin toxicity.
An overdose refers to taking too much melatonin at once, while toxicity refers to the accumulation of melatonin in the body over time. Melatonin toxicity is rare and usually only occurs in people with pre-existing liver or kidney problems.
In summary, taking too much melatonin can result in unpleasant side effects and pose risks over a long period.
More on this soon but also we must look at;
Factors that Affect Melatonin Dosage
The appropriate dosage of melatonin can vary depending on individual factors.
Some of the key factors that can influence the dosage of Melatonin may include:
- Age: As previously mentioned, the recommended dosage for melatonin varies by age. Children and adolescents typically require lower doses than adults.
- Body weight: Individuals with a higher body weight may require a higher dosage of melatonin to achieve the desired effect.
- Health status: People with certain health conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, may need to adjust their melatonin dosage to avoid any potential complications.
- Medication use: Some medications, such as blood thinners and antidepressants, can interact with melatonin, affecting its effectiveness and potentially causing side effects.
- Other supplements: Taking other supplements that affect sleep, such as valerian root or chamomile, may influence the appropriate dosage of melatonin.
It’s important to note that individual factors can vary widely, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to melatonin dosage.
Consulting a healthcare provider before taking melatonin supplements can help ensure that the dosage is appropriate for your individual needs and reduce the risk of potential complications. A healthcare provider can also help identify any potential drug interactions or health concerns that may affect the dosage.
The Problem With Melatonin Supplements
The incredible thing about melatonin is when this hormone is naturally produced this is only estimated to be about 10–80 MICROGRAMS per night.[8]
80 MICROGRAMS is the equivalent of 0.08mg, just under 0.1mg which is a lot less than your typical 3mg dose from Melatonin supplements and people generally produce a lot less so this is quite interesting.
So based on claims that people are overdosing on Melatonin this information does give it some merit. Mostly because of what has been found to be the case with melatonin supplements and how people find themselves having to increase their dose. This can not only lead to addiction but the more melatonin taken in supplement form the less is produced naturally.
0.5g is considered a low dose of melatonin by healthcare professionals but even this is well over 5x what the body naturally produces. Many will claim that these (what they think are) low doses do not work well enough although this is actually another problem – what is in these capsules very often is a lot more than what is stamped on the pill.
Now, I don’t know if this is completely true. Maybe it is or maybe it isn’t but it does appear that there are much better alternatives to melatonin supplements. Each to our own but seriously!
So What Is The Solution?
Like many adverse health conditions, sleep deprivation can be resolved by the right nutrients in your diet. Foods that contain Tryptophan, Melatonin, and sources of Magnesium should really be your first port of call before taking supplements;
Some examples of Food Sources I will share below. These lists come from MedicinePlus.gov and theSleepDoctor.com
So according to source #1 Tryptophan can be found in:
- Cheese
- Chicken
- Egg whites
- Fish
- Milk
- Sunflower seeds
- Peanuts
- Pumpkin seeds
- Sesame seeds
- Soybeans
- Turkey
Whilst according to Souce #2 Melatonin can be found in the following food sources;
- Milk
- Pistachios – Other Nuts contain Melatonin too but Pistachios are the best.
- Tart Cherries
- Fatty Fish
- Rice
- Goji Berries
- Oats
- Mushrooms
- Corn
- Bananas
Also, Seeds and Nuts contain Magnesium and Zinc so these are another great source. But…
Can Other Supplements Help?
When it comes to Sleep Support supplements typically their ingredients can work really in two different ways. One is to calm you down. Many struggle to sleep not because of Melatonin deficiency but because of things like stress and racing thoughts. So here ingredients such as Lemon Balm, Passionflower, and GABA may be helpful.
Alternatively, many supplements will either include a dose of melatonin or other ingredients like 5-HTP to help along with natural production. You should also find ingredients such as B Vitamins to help absorb the other ingredients into the bloodstream.
I would personally only recommend supplements if a diet including the different food sources above is not helpful but if you are keen to try supplements check out some of our sleep supplement reviews below;
- Dream Optimizer Review – Low Dose Melatonin Sleep Spray
- HFL Deep Sleep Formula – Complex Nutritional Blend with many unique Ingredients
- BrainMD Restful Sleep Formula – Top Rated Company for Brain Health and Nootropics
In Conclusion
Melatonin is a natural hormone that plays a critical role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. While melatonin supplements are generally safe, it’s important to take them within the recommended dosage to avoid potential risks and complications.
Taking too much melatonin can result in unpleasant side effects and pose risks over a long period. Factors such as age, body weight, health status, medication use, and other supplements can influence the appropriate dosage.
So consulting a healthcare provider before taking melatonin supplements can help ensure that the dosage is appropriate for your individual needs and reduce the risk of potential complications.
In summary, understanding safe dosages of melatonin is crucial for maximizing its benefits and minimizing potential risks. By following the recommended dosage and consulting with a healthcare provider, you can take advantage of melatonin’s sleep-promoting effects and improve your overall quality of life.
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Melatonin dosage: What amount is safe? https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/expert-answers/melatonin-side-effects/faq-20057874
- National Sleep Foundation. (2021). Melatonin and Sleep. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/nutrition/melatonin-and-sleep
- Drugs.com. (2021). Melatonin Dosage. https://www.drugs.com/dosage/melatonin.html
- WebMD. (2021). Melatonin: Side Effects, Uses, Dosage, and More. https://www.webmd.com/vitamins-and-supplements/melatonin-uses-and-risks
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2020). How much melatonin is too much? https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/how-much-melatonin-is-too-much





Anxiety and Depression best ways to lower blood sugar BiOptimizers blood pressure supplements blood sugar support supplements Digestive Enzymes Supplement digital products Dr Sam Robbins Erectile dysfunction Exercise Gut Health Healthy Living heart health HFL how to lower blood sugar levels How To Lower Cholesterol insulin resistance joint health supplement Keto keto dieting Keto Diet Weight Loss leaky gut supplements leptin resistance list Magnesium deficiency Matt Gallant mental health multivitamins Nootropics nutrient supplements Probiotics Probiotic Supplements proteolytic enzymes reverse type 2 diabetes stress and anxiety stress relief vitabalance vitapost Wade Lightheart weight loss articles weight loss diet plans weight loss product reviews weight loss supplements weight loss supplements that work weight loss tea