During a recent study, it was revealed that serum Zonulin levels in patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) were elevated, comparable to those found in individuals with celiac disease and Gluten Intolerance.
These findings suggest that serum zonulin could potentially be used as a biomarker to detect altered intestinal permeability (Leaky Gut Syndrome) in IBS patients. But what is Zonulin and How Does It Affect Leaky Gut Syndrome?
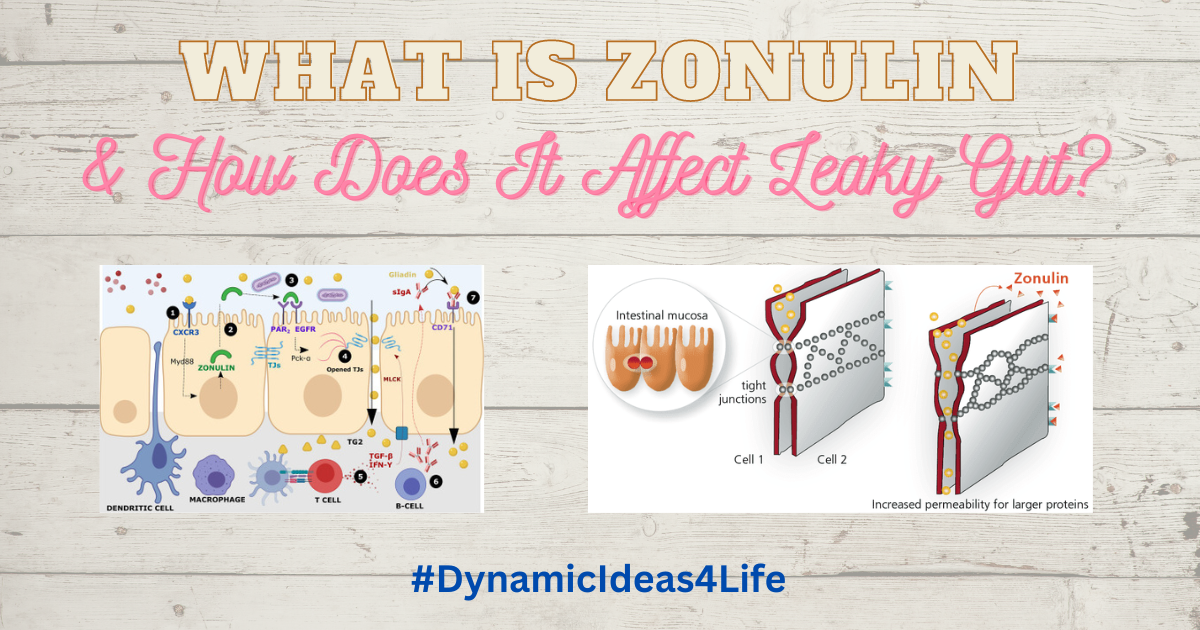
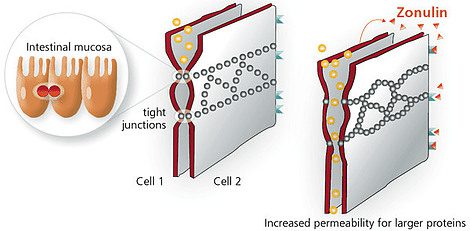
So, Zonulin is a protein. It works by regulating the tight junctions between cells in the gut lining.
These tight junctions act as gatekeepers, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the gut.
However, when zonulin is activated more than it needs to be this causes the tight junctions to become more permeable, allowing larger molecules to pass through.
When this happens this is what we call “leaky gut syndrome” because when this occurs these larger molecules start to create holes in the gut lining that allow fluids such as bile and stomach acid to pass through.
Which in turn can lead to further health problems, including autoimmune disorders, chronic inflammation, and food sensitivities such as Gluten/Casein Intolerance.
So I have covered this in a few articles now but let’s explore this a bit further to make this more clear.
What Is Zonulin and How Does It Affect Leaky Gut?
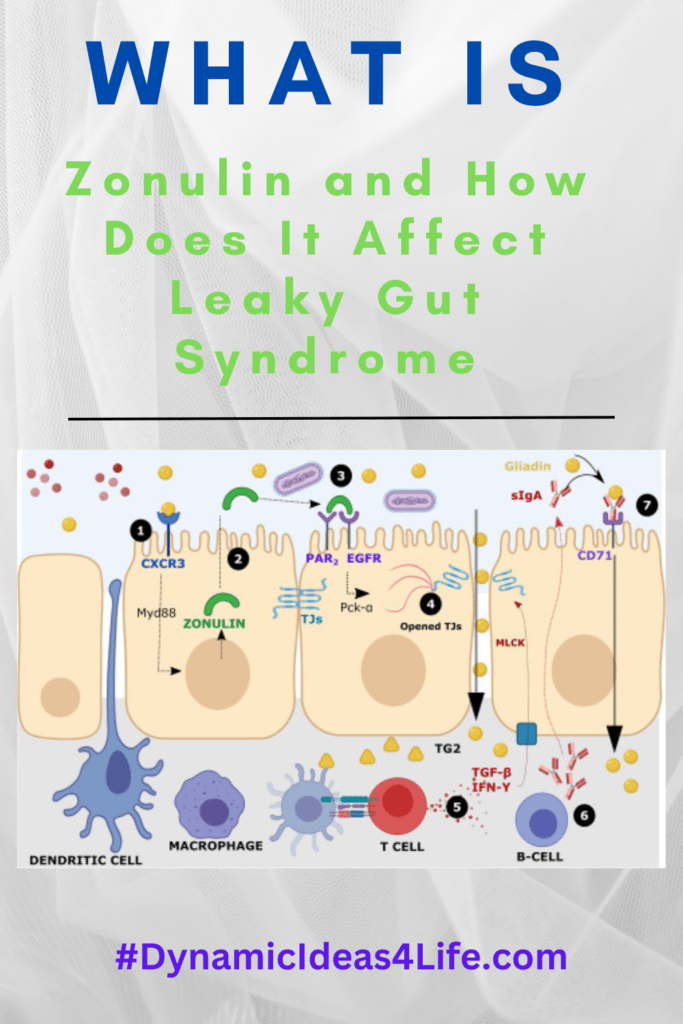
Now, for anyone that doesn’t know our gut lining is made up of a single layer of cells called enterocytes, which are held together by tight junctions. These tight junctions form a barrier that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the gut, allowing only small molecules to pass through.
This helps to prevent the entry of harmful substances into the bloodstream and ensures that the nutrients we need to stay healthy are absorbed efficiently.
In this regard, Zonulin is responsible for regulating the permeability of the tight junctions. Our body actually needs Zonulin for this purpose but when Zonulin levels are high, these tight junctions become more permeable, leading to increased gut permeability.
Over-stretched gut permeability as mentioned can result in larger molecules, including bacteria and undigested food particles, entering the bloodstream, which will then trigger a natural immune response.
This immune response can manifest in several ways but usually, this will lead to chronic inflammation. Something which has been linked to a range of health problems, including autoimmune disorders, allergies, and food sensitivities (eg. Gluten & Dairy Intolerance).
So, I know I am kind of repeating myself here but anyway…
How Zonulin Can Be Bad
Some studies taken in relation to this Intestinal Permeability have shown that people with autoimmune disorders and other chronic health conditions often have elevated levels of zonulin. This suggests that a leaky gut may be a contributing factor in the development of these conditions.
Additionally, having a leaky gut has been linked to an increased risk of food sensitivities, which are caused by undigested food particles that enter the bloodstream and trigger an immune response.
There are several factors that can contribute to increased zonulin levels and a leaky gut, including stress, a diet high in processed foods and sugar, and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen.
In order to maintain a healthy gut and reduce the risk of leaky gut and related health problems, it is important to adopt a healthy diet and lifestyle, manage stress, and avoid NSAIDs where possible.
Why Our Body Can Produce Too Much Zonulin
There are several factors that can contribute to elevated zonulin levels in the body, leading to an increased risk of leaky gut and related health problems. Some of the most common causes of increased zonulin production include:
- Gluten and other food triggers: Gluten and other food triggers, such as dairy, soy, and corn, can activate the Zonulin pathway and increase gut permeability.
- Chronic Stress: Chronic stress has been shown to disrupt the gut-brain axis and increase the production of zonulin.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as bacterial and viral infections, can trigger an immune response that increases Zonulin levels.
- Inflammation: Inflammation, whether due to injury, infection, or other causes, can activate the zonulin pathway and increase gut permeability.
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), can increase zonulin levels and disrupt the gut barrier.
Taking care to avoid these 5 triggers above is a good place to start but also it’s worth noting…
How To Test For High Zonulin Levels
There are two main ways to test for high zonulin levels to find out if this is a problem that is affecting you.
- Blood Tests: The most common way to test for elevated zonulin levels is through a blood test. This test measures the level of zonulin in the bloodstream and can indicate if there is an issue with gut permeability. Blood tests are simple and non-invasive, and can be performed by a healthcare provider in a clinical setting.
- Stool Tests: Stool tests can also be used to test for elevated zonulin levels by measuring the level of zonulin in the stool. Stool tests are more invasive than blood tests but can provide a more comprehensive understanding of gut health and gut permeability.
By comparison whichever test you take still It’s important to note that while these tests can indicate elevated zonulin levels, it is not a definitive diagnosis of leaky gut or other health problems.
With this in mind further evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a review of symptoms, medical history, and additional tests, is necessary for a proper diagnosis.
How To Naturally Lower High Zonulin Levels?
There are several ways to naturally lower high zonulin levels and improve gut health. Some of the most effective strategies include:
- Diet: Avoiding trigger foods, such as gluten, dairy, soy, and corn, can help reduce zonulin levels and improve gut health. Eating a diet rich in fiber and fermented foods, such as kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, can also support gut health.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can increase zonulin levels and disrupt gut health. Practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, exercise, and deep breathing, can help lower zonulin levels and improve gut health.
- Probiotics: Taking Probiotics can help maintain gut health and reduce zonulin levels. Probiotics can be found in fermented foods, such as kefir and sauerkraut, or in supplement form.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve gut health and reduce zonulin levels by reducing inflammation and promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
- Herbs and Supplements: Certain herbs and supplements, such as L-glutamine, licorice root, and quercetin, have been shown to support gut health and reduce zonulin levels.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for reducing high zonulin levels and improving gut health.
Factors such as age, overall health, and underlying medical conditions should be taken into consideration when developing a plan to lower zonulin levels.
Recommended Supplements
In regards to the information shared above other than a healthy diet, there are two products that I’ve previously reviewed on this website that I believe could be beneficial for getting zonulin levels under control and that may help to remedy Intestinal permeability.
These are as follows;
i.) Bioptimizers Biome Breakthrough (fka. Leaky Gut Guardian)

This supplement is from a brand that I know quite well having shared reviews already for most of their products. They also have a probiotics supplement P3-Om which may also be beneficial for Leaky Gut but Biome Breakthrough itself is a more tailored formula for helping to repair the damage of high Zonulin. Inside is a blend of IgY Max Hyper Immune Egg Powder, Bovine Bone Broth, Bovine Collagen, and Lactobacillus Probiotics.
You can also get a vegetarian formula without the Bovine ingredients but I would suggest if you are not vegetarian get the bovine type for added effect.
ii.) Touchstone Essentials Organic Super Fiber

This is another company that I feel is an authority in the market of supplements. Touchstone Essentials offers several health supplements including a zeolite detox formula and their own CBD product (Calm CBD) but one of their most recent additions is their Prebiotic Fiber supplement Organic Super Fiber.
So for anyone that doesn’t know prebiotic fiber is great for gut health is it helps to nourish probiotics in the gut microbiome. Eating brown rice and oatmeal are good examples of dietary fiber but taking this supplement on top can provide your gut with so much more.
This includes over 20 ingredients including protein-digesting enzymes which actually can be great for the effects of leaky gut as Zonulin itself is a protein and it can help remove excess zonulin from the body.
In Conclusion,
When zonulin levels are elevated, the tight junctions in the gut become more permeable, causing the gut to become “leaky.” This process can allow unwanted substances, such as bacteria and toxins, to pass through the gut and into the bloodstream, leading to a host of health problems.
Some of the most common health problems associated with high zonulin levels and a leaky gut include autoimmune disorders, chronic inflammation, food sensitivities, and digestive issues.
Fortunately, there are several steps that can be taken to lower zonulin levels and reduce the risk of a leaky gut and related health problems.
Here are a few effective strategies:
- Diet: A healthy, balanced diet is crucial for maintaining gut health and reducing zonulin levels. Avoiding trigger foods, such as gluten, dairy, soy, and corn, can help reduce inflammation and improve gut health. Eating a diet rich in fiber and fermented foods, such as kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, can also support gut health.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can increase zonulin levels and disrupt gut health. Practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, exercise, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and improve gut health.
- Avoid NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and aspirin, can increase zonulin levels and disrupt gut health. Avoiding or reducing the use of NSAIDs can help lower zonulin levels and improve gut health.
By following these strategies, you can reduce your risk of a leaky gut and related health problems and maintain a healthy gut. However, it’s always best to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for reducing zonulin levels and improving gut health.
Your healthcare provider can help you determine the best approach based on your unique needs, medical history, and overall health. If you believe you could have high zonulin or leaky gut then definitely speak to them.
Getting treatment for this condition is very important so definitely do not overlook this!
Final Word
Just before I go I hope you have found today.s content helpful. If you would like to share your thoughts, feedback, or questions then please do so in the comments section below. I will be more than happy to try and answer.
Also, if you have found this content helpful today then please give this a share with anyone that you may think would like to read this.
Many thanks and #StayDynamic
All the best;
Alex B. Chivers
DynamicIdeas4life.com
Contact us at: chivs86@dynamicideas4life.com
#Zonulin, #LeakyGuy, #IntestinalPermeability, #GutHealth, #Digestion
References
- Fasano, A. (2012). Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1258(1), 25-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06538.x
- Lopetuso, L. R., Scaldaferri, F., Bruno, G., Petito, V., Franceschi, F., Gasbarrini, A., & The Gut-Brain Axis in Health and Disease: Focus on the Gut Microbiota (2018). The therapeutic management of gut barrier leaking: the emerging role for mucosal barrier protectors. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences, 22(3 Suppl), 53-62. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201802_14323
- Fasano, A. (2011). Zonulin and its regulation of intestinal barrier function: the biological door to inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Physiological Reviews, 91(1), 151-175. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00003.2008
- Wang, W., Uzzau, S., Goldblum, S. E., & Fasano, A. (2000). Human zonulin, a potential modulator of intestinal tight junctions. Journal of Cell Science, 113(Pt 24), 4435-4440. PMID: 11082039
- Leaky Gut Syndrome. (2017). Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/leaky-gut-syndrome
- Bischoff, S. C., Barbara, G., Buurman, W., Ockhuizen, T., Schulzke, J. D., Serino, M.,… & Wells, J. M. (2014). Intestinal permeability-a new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterology, 14(1), 189. doi: 10.1186/s12876-014-0189-7